Ulcers are a common ailment that affect many people around the world. They are characterized by a sore that develops on the skin or mucous membranes. Ulcers can occur in various parts of the body, including the stomach, mouth, and genital area.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments for ulcers, as well as some tips for managing the condition.
CAUSES OF ULCERS
Ulcers can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Infection: The bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a common cause of stomach ulcers.
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen, can cause stomach ulcers.
Stress: Emotional stress can increase the risk of developing ulcers.
Alcohol and tobacco use: Heavy alcohol consumption and smoking can irritate the lining of the stomach and increase the risk of ulcers.
SYMPTOMS OF ULCERS
The symptoms of ulcers vary depending on the location of the sore. Some common symptoms include:
Abdominal pain: Stomach ulcers can cause a dull or burning pain in the abdomen.
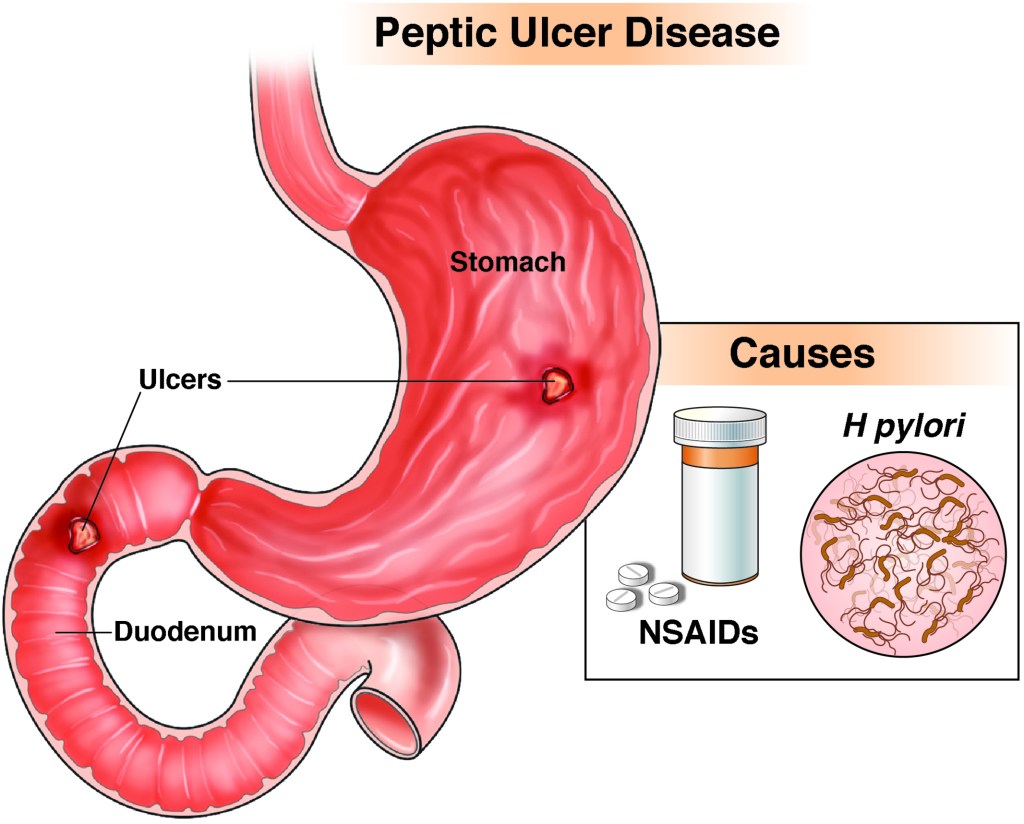
Indigestion: Ulcers can cause bloating, heartburn, and nausea.
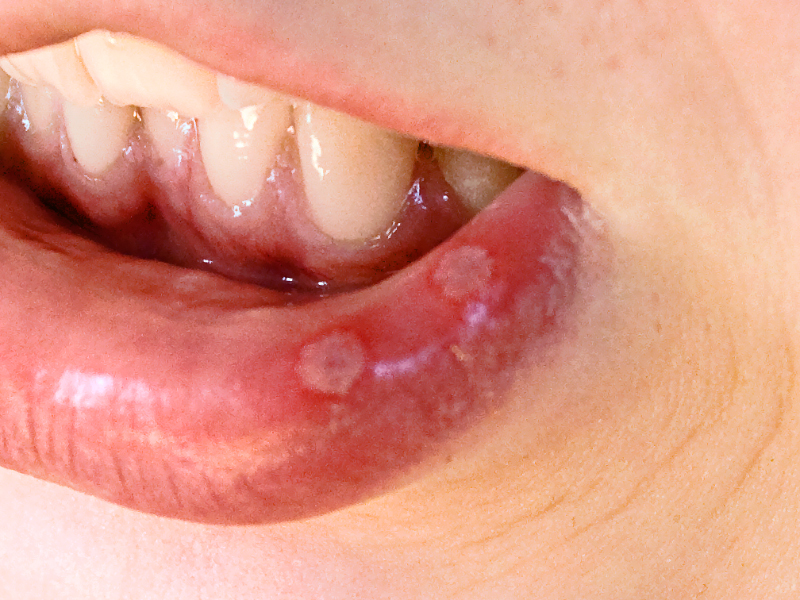
Mouth sores: Ulcers in the mouth can cause pain, swelling, and redness.
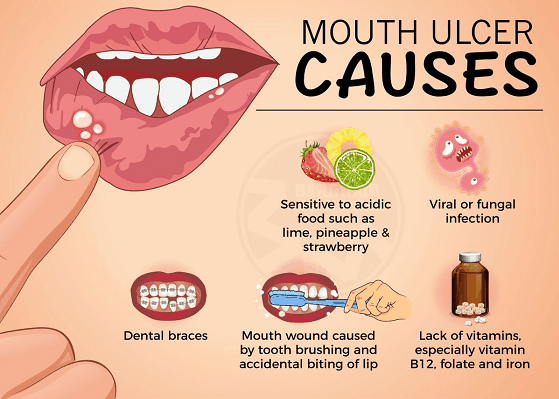
Genital sores: Ulcers in the genital area can cause pain, itching, and discharge.
TREATMENT OF ULCERS
The treatment of ulcers depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Some common treatments include:
Antibiotics: If the ulcer is caused by an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed.
Medications: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 blockers can help reduce stomach acid and relieve symptoms.
Lifestyle changes: Avoiding alcohol and tobacco, reducing stress, and eating a healthy diet can all help manage ulcers.
MANAGING ULCERS
In addition to medical treatment, there are several things you can do to manage ulcers:
Avoid trigger foods: Spicy, acidic, and fatty foods can all irritate the stomach lining and make symptoms worse.
Eat small, frequent meals: Eating smaller meals more frequently can help reduce acid production and prevent symptoms.
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help reduce stomach acid and promote healing.
Manage stress: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, can help reduce stress and prevent symptoms.
CONCLUSION
Ulcers are a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. While they can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful, they are usually treatable with medication and lifestyle changes. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can help manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life